[ad_1]

June 3, 2019 — Festo brings to Robotics Summit/DeviceTalks Boston 2019, June 5-6 at Seaport World Trade Center, Boston, solutions which are intended to reduce engineering effort and shorten time to market for robotic systems, including laboratory automation. Festo also displays at Booth #216 a hands-on bionic learning kit for middle and high school students.
Topping off its display, Festo flies the Bionic Learning Network flying insects: the BionicOpter dragonfly and independent-group-flight eMotion butterflies. Flights are scheduled for June 5 from 5-6 p.m. and June 6 from 11-11:30 a.m. at the Festo Booth.
Festo has studied the flight characteristics of the dragonfly, employing lightweight construction and function integration. The BionicOpter can fly in all directions, hover in mid-air, and glide without beating its wings. eMotion butterflies combine the ultralight construction of artificial insects with the coordinated flying behavior of a collective. Ten cameras record the butterflies using the robots’ infrared markers. The cameras transmit the position data to a central master computer, which coordinates the butterflies group flight. The intelligent networking system creates a guidance and monitoring system that could be used in the networked factory of the future.
With the Festo Handling Guide Online, engineers can design single axis, 2D, or 3D Cartesian robots and receive CAD files. The robots are delivered either as subassemblies or as kits. The Festo Motion Control Package (FMCP) designs the robot’s control panel utilizing data generated from the Handling Guide Online session.
Festo also demonstrates a laboratory automation application for liquid dispensing utilizing a Cartesian robot liquid valve manifold. In this demonstration, an EXCM planar surface gantry equipped with a VTOE eight-liquid valve manifold with 9 mm pitch channel fills an entire row of microwell plates simultaneously. One valve for each nozzle allows for independent control of each of the eight channels. The EXCM planar surface gantry is suitable for any space constrained pick-and-place, assembly, and laboratory automation application.
The linear axes ELGC and mini slide EGSC electric actuators are used for applications where compact dimensions are essential. These axes can be combined into space-saving handling systems that fit seamlessly into assembly, test and inspection, small parts handling, and desk top applications. They offer a ratio between installation space and working space. The axes and mini slide feature a common system approach, platform architecture, and adapter-less connections.
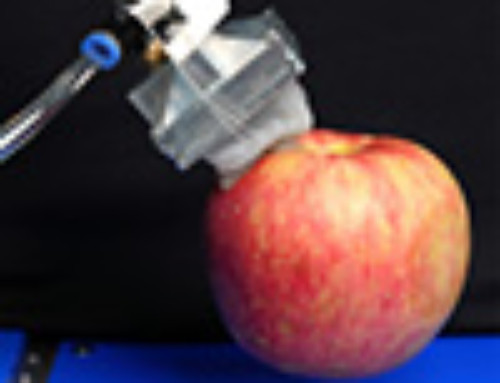
The DHEF adaptive shape gripper offers gripping flexibility. The adaptive shape gripper automatically grips mixed objects with multiple shapes, unaligned objects, and numerous objects at once. The gripper gently forms around an object and is ideal for gripping fragile items. It is suitable for human/machine interaction. The DHEF adaptive shape gripper is the industrial version of the Bionic Learning Network’s FlexShapeGripper, which models the gripping mechanics of a chameleon’s tongue. The lizard’s tongue darts out at its prey and then pulls it in while the outside edges wrap around the target, securely holding it. The DHEF adaptive shape gripper uses a silicone cap as the tongue device that draws an object in and captures it.
Festo shows adaptive gripper fingers DHAS for transferring or sorting fragile, oddly shaped, or tightly packed products. Applications include transferring parts from tight packaging, handling sensitive parts such as filter cartridges, picking unevenly shaped products such as avocados, moving parts to humans at manual assembly stations, conforming to parts with various diameters, and more. The concept of the DHAS derives from the flexible movement of a fish’s tail, what Festo calls the Fin Ray Effect. The gripper fingers wrap around objects with a wave-like motion. Traditional parallel grippers will also be on display.
The Festo EHMD rotary gripper module is designed for laboratory automation applications such as fitting and removing vial caps. The EHMD also picks and places small parts from trays. With the addition of the CMMO-ST motor controller, the EHMD module delivers gripping under power. Gripping can be implemented either electrically with a stepper motor or pneumatically utilizing a cylinder.

Check out our free e-newsletters
to read more great articles.
Subscribe Now
[ad_2]
Source link




Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.